Why do Mortgage Interest Rates Change and What Influences Them?

Buying a home can be a stomach-churning process if you’re watching and waiting for interest rate changes. Odds are you’re fretting over nothing.
Interest rates are only one factor of many in your decision to buy a home. While you should take time to educate yourself on why interest rates change, don’t forget to look at the whole picture. There's a lot more that goes into a home purchase, including location, closing costs, down payment, and listing price.
When is the right time to buy a home?
Is now a good time to buy a home or wait a bit longer to see if rates decrease? While mortgage interest rates rise and fall for a variety of reasons (more on that below), they generally don’t move much. And even then it’s not expected to matter much in the long-run: a quarter-point change isn’t likely to alter the monthly payment on your mortgage by more than $20-$30, at the most.
“The right time to buy a home or condo is when you’ve found a good property in a good neighborhood where prices are on the rise. If you’re planning to be there for at least five years, make the move and don’t look back,” says Jonathan Payne, American Financing’s Director of Operations.
You also have more control than you might think. A top lender will give you options on the rate, the deadline, and the closing costs. Make sure you can realistically afford the deal before moving forward. Once you lock, the rate you choose is good for up to 60 days.
6 things that influence mortgage interest rates
When should you lock? There’s no hard science to the process, but there are guidelines you can follow. Here's a closer look at what can influence changes in any given week:
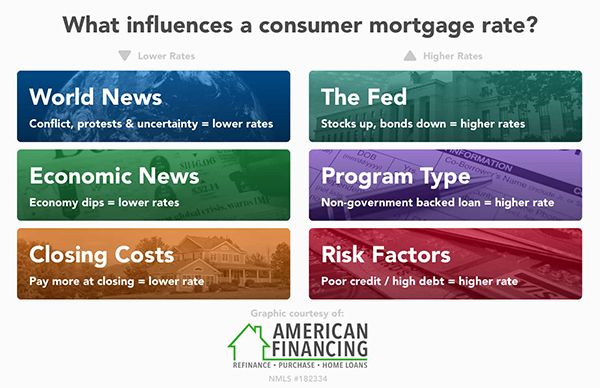
World news
Believe it or not, global news affects US stock and bond prices. Generally, bad news and uncertainty in the world are good for mortgage interest rates. Investors tend to flock to bonds in bad times because bonds are safe places for investments. The demand for bonds pushes interest rates lower, which in turn benefits home buyers.
Economic news
The economy is another reason why interest rates change. That’s because central banks use their authority to set interest rates as a tool to influence the pace of a nation’s economy and the rate of inflation. When the economy dips, our central banks lower interest rates to promote more economic activity.
However, interest rates will rise if the economy shows signs of overheating — meaning a prolonged period of healthy economic activity leading to high levels of inflation from increased consumer wealth. It’s an attempt to lower the amount of spending and borrowing to prevent a recession.
Closing costs
Closing costs are typically between 2% and 5% of the loan amount depending on several factors, including the loan type, your mortgage lender, where you live, and the principal amount borrowed. If you choose to finance your closing costs, the monthly loan payments will be higher than if you paid the closing costs out-of-pocket. So, the more you pay at closing, the less you pay in interest over the life of your loan.
The Federal Reserve (Fed)
The Federal Reserve (Fed) is the central bank of the United States. It makes a lot of important decisions regarding monetary policy, financial stability, and consumer protection.
One of its primary responsibilities is setting short-term interest rates to control inflation and avoid recession. Given that, many people think the Fed is the reason why interest rates change. While they don’t raise mortgage rates per se, they can increase the federal funds rate, which is used as the benchmark for a range of consumer interest rates (credit cards, cars, and mortgages).
They also influence the rate of bonds to which mortgage interest rates are tied. As stocks go up, bonds tend to go down, and that can mean higher rates.
Loan program type
Interest rates change based on your selected loan program. There are fixed-rate mortgages and adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs), government-backed loans, conventional loans, jumbo loans, etc. Benefits vary, but for the sake of this article, let’s go over options that offer the most competitive rates.
You’re likely to find significant savings when selecting a government-backed loan (FHA, VA, USDA) because the lender is guaranteed to get their money back if the borrower ever defaults. If you choose a non-government-backed loan (15 or 30-year conventional), be prepared to receive a higher rate.
Bonus tip: if you’re looking to move within five years, consider a 5/1 ARM. You’ll receive a fixed, low-interest rate for the first five years, but it will fluctuate (and rise) after the introductory period ends.
Personal risk factors
Last but not least, your financial habits can also determine the interest rate you receive. Think credit score, debt-to-income (DTI) ratio, and your overall debt in general. If you’re responsible with debt — you pay it on time and keep a reasonable balance on credit cards — you’re likely a good-looking candidate in the eyes of a mortgage lender. Do what you can to increase your credit score. Pay down credit card balances. Keep from adding (or eliminating) lines of credit. You’re sure to find the best deal on a mortgage if you take care of your finances.




